Understanding INAD
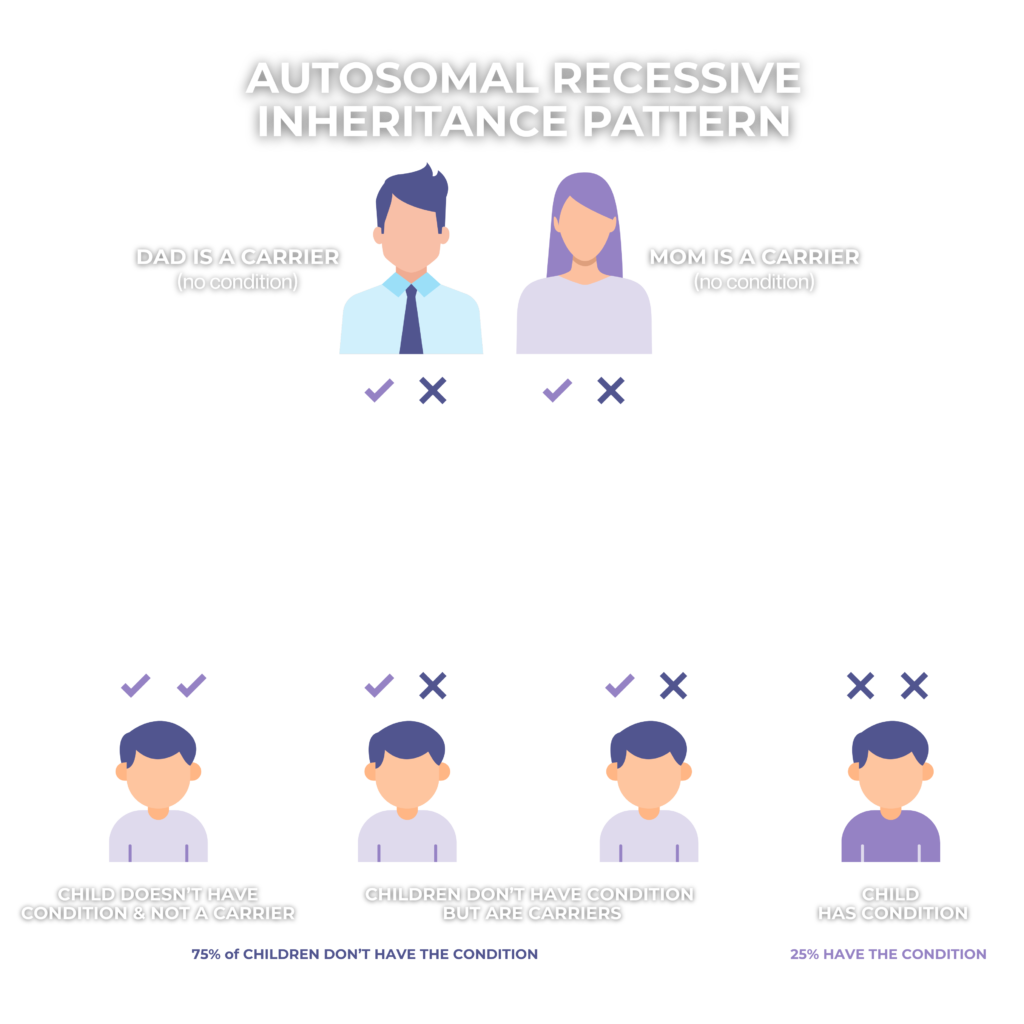
Infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy (INAD) is a rare, autosomal recessive, neurodegenerative disorder that affects young children, causing a progressive loss of motor and cognitive skills. It is classified under Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation (NBIA) disorders and is also considered a subset of PLAN (phospholipase-associated neurodegeneration). INAD is associated with disruptions in phospholipid remodeling and disruptions in recycling fatty acids, which contribute to the formation of spheroid bodies in nerve endings, ultimately leading to progressive neurodegeneration.